Plate heat exchangers
Detachable Plate Heat Exchanger
A detachable plate heat exchanger (PHE) is a device where heat exchange occurs between two liquids (working media). This process takes place in a plate pack. Hot and cold liquids flow counter-currently through the plates. Each plate has a gasket to prevent fluid mixing.
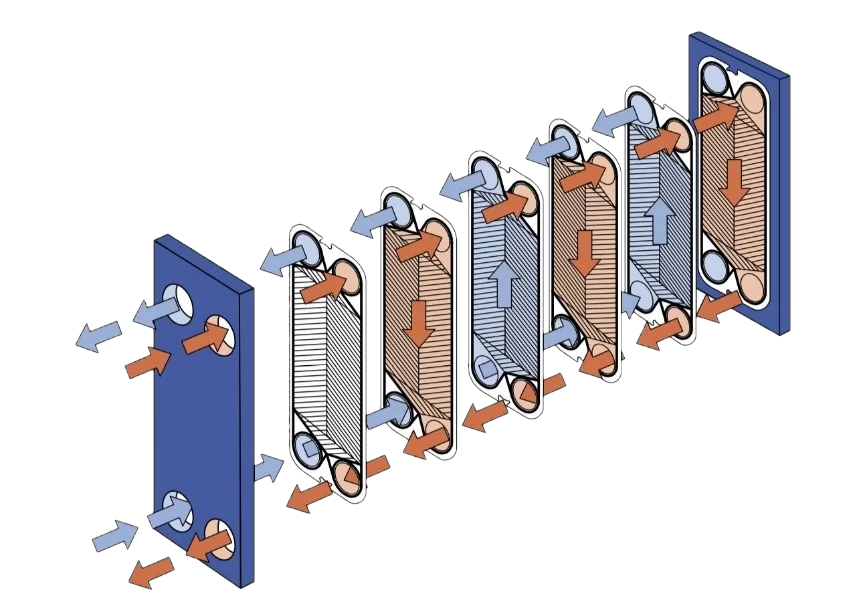
Plate Heat Exchanger Plates
Various liquids can act as working media. Plates are individually selected for each fluid type and temperature regime. They are typically made from:
- AISI304 – low-carbon stainless steel resistant to high temperatures and acids;
- AISI316 – corrosion-resistant alloy. Enhanced with nickel, molybdenum, and titanium for high-temperature endurance;
- SMO 254 – for aggressive environments. Alloy with chromium, nickel, copper, and vanadium additives for strength and durability;
- Titanium – for highly aggressive media.
There are 2 main types of corrugation angles:
- Sharp – low heat transfer (low heat transfer coefficient), low hydraulic resistance;
- Blunt – high heat transfer with hydraulic losses.
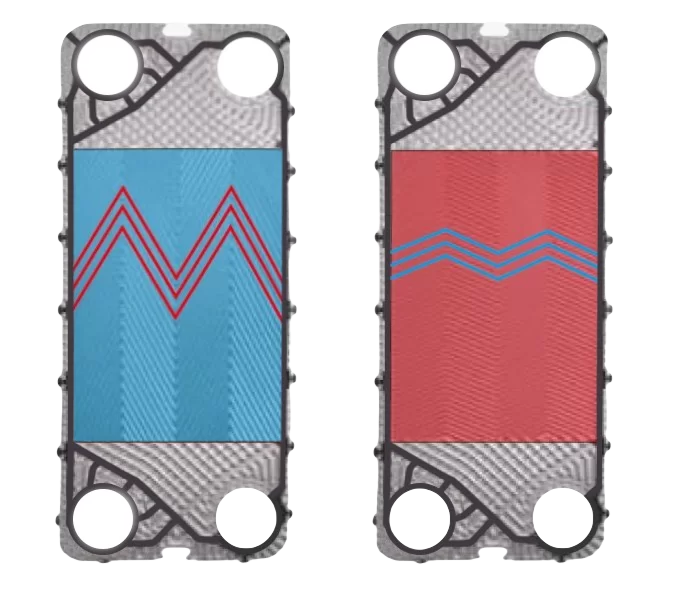

Gaskets (or seals) are installed between plates. They isolate and direct adjacent fluid flows while preventing leaks. Like plates, gaskets are selected based on compatibility with each fluid and temperature conditions.
- EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer). Foamed rubber;
- Viton (FPM, FKM) – fluorocarbon rubber with bisphenol additive;
- NBR (Nitrile Butadiene Rubber) – nitrile rubber.
| EPDM | Viton(FPM,FKM) | NBR | |
| Operating temperature | -20 to +150 | -20 to +190 | -20 to +130 |
| Max. temperature | 140-160 | 180-200 | 120-140 |
| Fluid Compatibility | |||
| Nitrogen | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Ammonia gas/nitrite/nitrate | 1 | 4 | 1 (except hot gas) |
| Acetylene | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Acetone | 1 | 3 | 4 |
| Gasoline | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| Benzene | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Boric acid | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Bromine | 4 | 1 | 4 |
| Butane | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| Water | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Hydrogen gas cold/hot | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Glycerin | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Fuel | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| Diesel fuel | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| Dry-cleaning fluids | 4 | 1 | 3 |
| Aluminum-based fluids | 1 | 1 (except acetate) | 1 |
| Automatic transmission fluid | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| Brake fluid | 1 | 4 | 3 |
| Fatty acids | 4 | 1 | 2 |
| Potassium chloride, cyanide, sulfite, sulfate | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Calcium chloride/sulfide/nitrate | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Sodium carbonate (soda ash) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Castor oil | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Kerosene | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| Coconut oil | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| Corn oil | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| Citric acid | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Butter | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Methanol | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Methyl alcohol | 1 | 4 | 1 |
| Mineral oil | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| Lactic acid hot | 4 | 1 | 4 |
| Lactic acid cold | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Cleaning solutions | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Soap solutions | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Natural gas | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| Olive oil | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Hydrogen peroxide (90%) | 3 | 2 | 4 |
| Baking soda | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Propane | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| Silicone oil | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Petroleum-based lubricants | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| Saltwater | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Concentrated hydrochloric acid | 3 | 1 | 4 |
| Copper sulfate | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Carbon dioxide, wet/dry | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Cottonseed oil | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| Wet chlorine | 4 | 1 | 4 |
| Dry chlorine | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| Chlorine-salt solution | 4 | 1 | 4 |
| Sodium chloride/cyanide | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Alkaline solutions | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Epoxy resins | 1 | 4 | 0 |
| Ethanol | 1 | 3 | 3 |
Why Choose a Detachable Plate Heat Exchanger?
Advantages:- Low production, installation, and commissioning costs, positively impacting the final price;
- Performance is easily adjustable by changing the number of plates;
- Maintenance and repairs require only one trained technician, not a full team;
- Compact design saves space;
- The heaviest part is the frame (tie rods and pressure plates), while the plate pack itself is lightweight. Compared to other heat exchanger designs, detachable PHEs have the lowest weight.
Types of Heat Exchangers by Flow Configuration
Plate heat exchangers are classified by refrigerant flow patterns. There are two main types: single-pass and double-pass. Three-, four-, and five-pass models also exist.
Key variants:
- Single-pass PHE
- Double-pass PHE
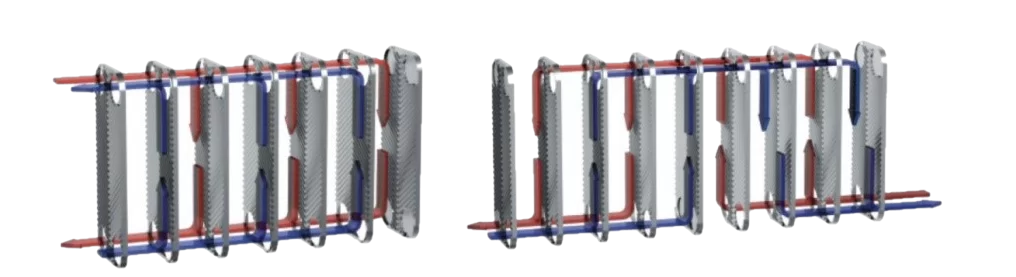
How to Select the Right Detachable Plate Heat Exchanger
Selection requires the following initial dаta:
- Power, kW;
- Flow rates per side, m³/h or kg/h;
- Inlet/outlet temperatures for both circuits, °C;
- Fluid names (media in circuits).
Related images




Any Questions Left?
Get a Free Consultation
Call Us or Request a Callback
(+994 50) 224 46 39(+90 543) 176 09 64
24/7 Active

